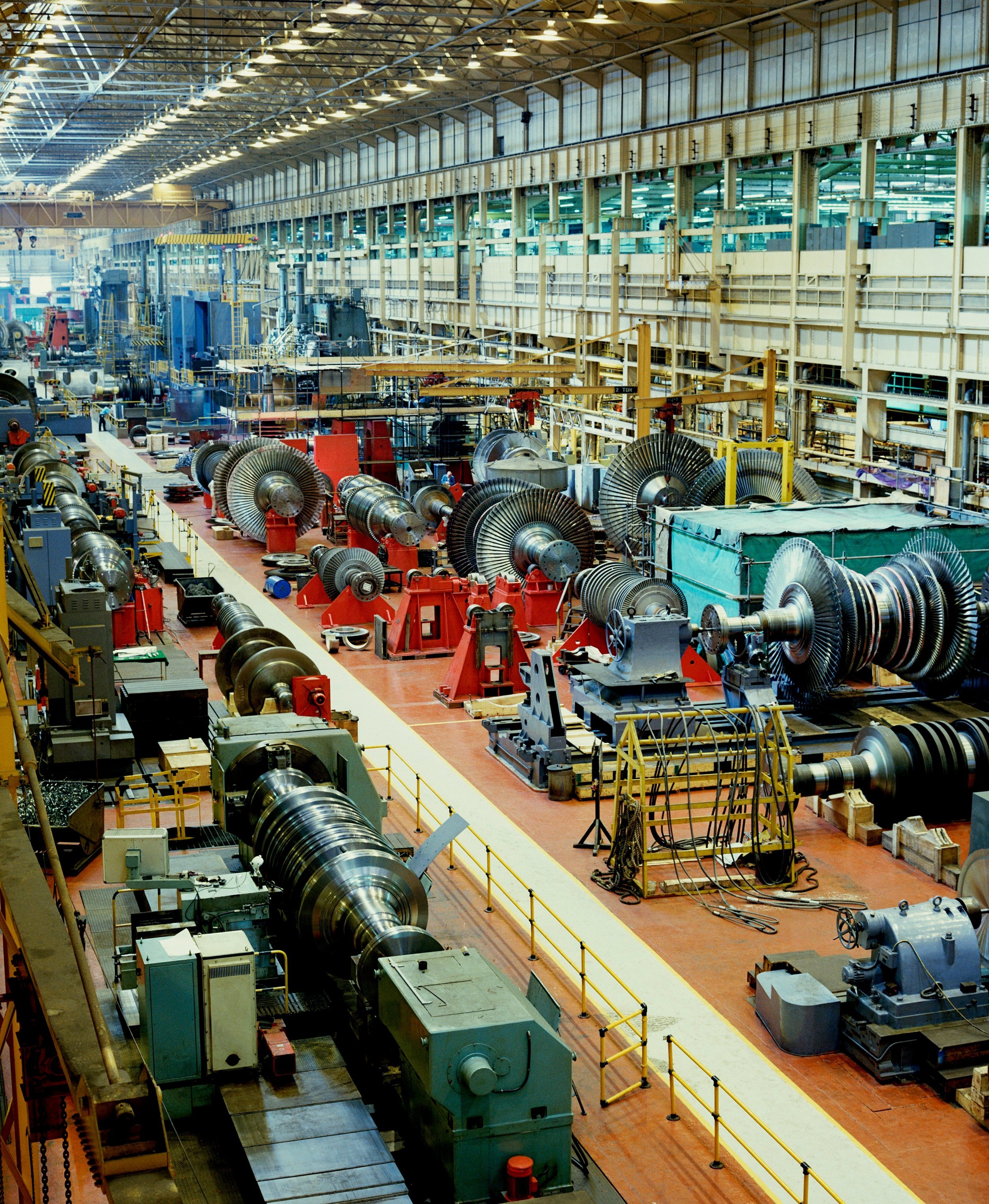
NRTC AUTOMATION BLOG | INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS AND AUTOMATION
What is Digital Manufacturing?
Digital manufacturing is the future of production and automation.
Digital manufacturing is the future of production and automation.
Manufacturing has traditionally been a numbers game: giant assembly lines mass producing products in vast quantities. Mass production is no longer the predominant model.
Manufacturing is trending towards a different future—one in which products can be produced on a dime and respond to changes in customer demand. Consumers are demanding higher-quality, customizable products, and on-demand products.
The result of demands placed on manufacturing is two-fold:
Lifecycle Churn: Consumers replace their products more often. In fact, one-third of home appliances and 60 percent of TVs are replaced with a better product, even when they continue to function. If companies want to keep up with consumer demand, they’ll need to constantly innovate and launch new SKUs.
Greater Customization: Mass production strategies cannot efficiently produce customized products. For example, a line of drones may be produced for a variety of applications. Each SKU will require different hardware, software, and systems which leads to multiple short production runs for each model.
The digital revolution in manufacturing is essential for satisfying these emerging demands.
What is Digital Manufacturing?
With the emergence and refinement of new and traditional technologies, manufacturing is becoming a multi-disciplinary field. Digital manufacturing, in particular, is becoming more prevalent across industries.
Digital manufacturing is an interdisciplinary approach, combining elements of design for manufacturability (DFM), computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM), flexible manufacturing, and lean manufacturing.
Digital manufacturing is the co-creation of product and manufacturing processes using a computer system. By linking systems and processes across production, the computer system is able to model and iterate on manufacturing designs and processes before creating the final product or assembly line layout.
An automotive original equipment manufacturer (OEM), for example, can model its manufacturing process (including tooling, assembly, and factory layout) while designers iterate on the next car lineup. Product and manufacturing designers can collaborate throughout the product life cycle, catching mistakes and identifying constraints early.
Types of Digital Manufacturing
DIGITAL MANUFACTURING LIFECYCLE
The digital manufacturing lifecycle is composed of three main parts: product, factory, and value chain management. Each aspect of the lifecycle is tied to manufacturing execution.
First, the product lifecycle includes engineering design, sourcing production, and service life. Digital data is utilized and necessary revisions to the design are subsequently made during that stage.
The smart factory leg uses automation and industrial internet of things (IIoT) technologies such as smart machines, sensors, and tooling. IoT provides instant feedback during operation, allowing greater visibility, control, and optimization. Enhanced business intelligence systems perform in-depth analysis, leading to insights into areas of performance or process improvement.
Value chain management aspects refer to optimizing for process and inventory while assuring quality. The result is decreased inventories, optimal process integration, and better customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Digital Manufacturing
Digital manufacturing strategies help companies recognize the benefits of product lifecycle management (PLM) in a number of ways. At its core, the main benefits are related to producing more, faster, and at a lower cost.
The benefits of digital manufacturing include:
Reduction in manufacturing waste: It’s estimated that 68 percent of manufacturers have reduced their bottom line as a result of excess materials, labor, packaging, and shipping. Through design modeling and optimization, predictive analytics, as well as an efficient response to demand. For example, digital data may be shared with contracted manufacturers to order just the right number of items, avoiding waste.
Mass customization: The use of computer-assisted control (CAD) and automation allows customization of product SKUs, without iterating on the production line. The result is the ability to continuously iterate on designs and manufacture products in smaller batches. Additionally, companies can utilize software to manage production, rendering low volume production runs more economical.
Avoidance of costly errors as a result of missed or misinterpreted data
Facilitation of more efficient factory lineups and models, with optimum layout
Enablement of quality data sharing through CAD-based machine inspections for industrial robots and machine tools
Improved visibility: IIoT sensors allow real-time visibility into the process, equipment, and systems. Technicians can optimize machine use and perform preventative maintenance using remote monitoring technology. Additionally, machine data can also be integrated with other data sets to optimize production—including the entire supply chain.
More rapid pace of innovation and enablement of six-sigma and lean initiatives by analyzing dimensions with a graphical environment. For example, digital manufacturing can help automate time consuming processes, such as front-end engineering.
Take Advantage of Digital Manufacturing
Capitalizing on digital manufacturing is essential for companies of the future. Consumers will come to expect higher-quality products delivered on faster time frames for a lower cost.
The best way to get started with digital manufacturing is through small projects that impact safety, efficiency, or quality. Projects may be value-driven based on customer journeys to maximize ROI. Consider collaborating with manufacturing floor technicians who can identify the best projects and increase adoption.
Plan to scale only after completing a series of successful projects. First, deploy to a manufacturing line, and the plant level next. Finally, develop a strategic plan to overcome roadblocks and embed technologies into future plants. It’s also important to continuously develop and invest in new roles and capabilities through upskilling programs.
Ultimately, a successful strategy to scale digital manufacturing is focused on business value. According to Mckinsey, aspirations should be linked to real and specific business needs.
Industry 4.0
The digitization of manufacturing has been nicknamed “Industry 4.0” because it represents the fourth revolution to occur in manufacturing. Industry 4.0 builds on Industry 3.0, which is when computers were first introduced to manufacturing.
According to Mckinsey, pioneers of Industry 4.0 have recorded 30-50 percent reductions in downtime, up to 3 percent improvements in productivity, and 20 percent declines in quality cost. Manufacturers aren’t deploying technologies at the same rate: many organizations are stuck in “purgatory”: they have no strategy to scale across their network.
Failure to implement digital manufacturing technologies will render businesses stagnant in the near future. Digital manufacturing will someday become essential to remain competitive. Businesses that stay ahead of the curve will continue to have an edge.
GET AHEAD WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
5 Types of Industrial Robots
Learning more about industrial robots will help make automation easier for any manufacturer.
Learning more about industrial robots will help make automation easier for any manufacturer.
It’s estimated that nearly 45% of production can be automated with robots.
There’s a variety of industrial robots available to suit nearly every need. In order to choose which type of robot is best, it’s paramount to start from the paradigm of “form follows function”. In other words, the choice of robot form factor should be dependent on its purpose.
Because there’s a wide variety of tasks that can be accomplished with industrial robots, consequently, there’s a number of robot varieties available that are suited to different types of tasks.
Learn more about the advantages of each type of industrial robot below!
What is an industrial robot?
A widely accepted definition for an industrial robot by ISO 8373:2012 is “an automatically controlled, reprogrammable, multipurpose manipulator, programmable in three or more axes, which can either be fixed or mobile for use in industrial automation applications.”
Though industrial robots are available in various form factors depending on the task, the most common industrial robots are automated arms. These robots can be classified into a few different categories based on movement, application, architecture, and brand.
Types of industrial robots
The most common type of industrial robot is a stationary robot--meaning robots that are bolted to a surface such as a floor, ceiling, or walls. There are five main types of stationary robots (or “robotic arms”) available today that can accomplish tasks such as sorting, welding, and finishing. According to the International Federations of Robots, the five main types of industrial robots includes SCARA, Articulated, Cartesian, Delta, and Polar.
ARTICULATED ROBOT
Advantages: Joints allow flexibility of movement. As a result, a broad range of tasks may be performed.
Disadvantages: Articulated robots are more costly compared with other robot arms, and require more sophisticated control systems.
The most common industrial robot structure is the articulated arm, which accounts for 60% of installations worldwide, according to the International Federation of Robots. These robots resemble a human arm and have structures analogous to a shoulder, elbow, and wrist.
Articulated robots have between two to 10 joints which allows them a flexible range of motion to accomplish dynamic tasks. As the number of joints increases, the more “smooth” the robot’s motions become.
Typically, articulated arms can pivot six degrees of freedom. Although this is less than that of the human arm which can rotate seven degrees of freedom, the range of motion is sufficient for almost any task.
The robotic arm may be attached to a gripper, which is analogous to a hand. The gripper may be as simple as suction cups or as complex as hand-like structures with fingers that can grip and pick up objects.
Similar to robot type, the type of gripper is dependent on the task. Alternatively, grippers may be drill bits, sanders, lasers, and almost any type of specialized tool.
Because of their flexible range of motion allowed by joints, articulated robots have many applications. They are used most often for printing, packaging, welding, machine tending, material handling, and metalwork.
SCARA ROBOTS
Advantages: Cost-effective, accurate, and proficient in a variety of assembly approaches.
Disadvantages: Limited range of motion and less efficient than Delta robots
SCARA is an acronym for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm and describes robots with two parallel rotary joints. While SCARA robots are faster than Cartesian robots, they are less precise. Though they are able to move along all three axes, these robots specialize in lateral movements.
SCARA robots revolutionized small electronic manufacturing because of their small footprint, simplicity, and low cost. They are particularly well-suited for assembly applications. The “C” in SCARA stands for “compliance” and refers to the small amount of “give” in its horizontal plane. However, SCARA robots are rigid in their vertical plane, hence the naming structure of “selective compliance”.
SCARA robot’s selective compliance is helpful for inserting parts into single-planes like circuit boards. Fitting a part into a hole requires some rigidity that is not possible with other types of robotic arms. However, SCARA robots have lower weight limits and fewer degrees of freedom due to this design.
CARTESIAN (RECTANGULAR) ROBOTS
Advantages: Can be more cost-effective and have simpler controls, with greater accuracy.
Disadvantages: Can only move linearly in three dimensions.
Cartesian robots operate on three linear axes (forwards and backward, up and down, and side to side). They get their namesake because they operate on the Cartesian Coordinate system (X,Y, and Z). In other words, they move horizontally and vertically in each ninety-degree plane.
Cartesian robots are frequently utilized for material handling, 3D printing, packaging, drilling, and storage or retrieval. Because Cartesian robots only operate linearly in three dimensions, their actions are more accurate. Additionally, they are more cost-effective and have simpler controls.
Advantages: Quick and accurate motions.
Disadvantages: Weight and range of motion restrictions.
Delta robots are popular in the manufacturing of food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. Delta robots are frequently described as “spider-like” because they are crafted from jointed parallelograms connected to a base and are typically mounted above a workspace.
The Delta robot has sweet origins--it was originally created to pick up pieces of chocolate and place them in a box. Because of its light design, its motions are accurate and very fast.
POLAR (SPHERICAL) ROBOTS
Advantages: Simple control systems, long reach, and fast operations.
Disadvantages: Less flexibility compared with articulated arms and require larger footprints.
Polar robots, also known as ‘spherical robots’, possess an arm attached to two rotary joints and one linear joint. These robots move along polar coordinates, which allows a spherical range of motion.
The first industrial robot ever created was a spherical robot named “Unimate”. Unimate worked on General Motors assembly lines beginning in the 1950s, transporting die castings and welding parts onto auto bodies.
While still in circulation, polar robots are considered slightly obsolete technology that can be replaced by more versatile articulated robot arms. However, polar robots can still be more cost-effective.
When deciding on which type of robot to select, it’s most important to decide on the task or set of tasks it’s required to perform. Additionally, prospective robot owners will need to think about interoperability with existing infrastructure. With a range of options on the market, manufacturers can weigh the costs and benefits to decide on the best model for their needs.
AUTOMATE WITH NRTC
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Why is Manufacturing Important?
Although manufacturing accounts for only 12 percent of the U.S. economy, it has exponential and widespread impacts across the economy, societies, and humanity.
Although manufacturing accounts for only 12 percent of the U.S. economy, it has exponential and widespread impacts across the economy, societies, and humanity.
Throughout history, manufacturing has improved quality of life, enabled the growth of human populations and societies, and drives innovation through the efficient mass production of materials.
History of Manufacturing
While manufacturing may be associated with high-tech facilities and modern methods such as Lean, Six Sigma, and JIT, it actually began long before the emergence of Homo Sapiens.
PREHISTORY AND ANCIENT HISTORY
Stone tool making, also known as the “Oldowan Industry”, is at least 2.3 million years old. The manufacturing of stone tools was partially responsible for human evolution as a result of hunter-gatherer lifestyles.
The manufacturing of stone tools optimized over many eons. Though little is known about production over that period, archaeologists found the longest-producing manufacturing site in Africa. At the site, stones were processed on a ten-kilometer stretch between two mountains for around a million years.
Specialization and the division of labor began to emerge in toolmaking during the Neolithic age (70,000 BCE) and more advanced tooling occurred as early as 35,000 BCE.
In ancient times, Greek philosopher Xenophon observed division of labor.
“In a small city the same man has to build beds, chairs, ploughs and tables and often even to build houses. […] But in the big cities [an artisan will get] his living merely by stitching shoes, another by cutting them out, a third by shaping the upper leathers, and a fourth will do nothing but fit the parts together.”
The division of labor that Xenophon observed in large cities allowed ancients to produce goods faster, better, and cheaper.
Manufacturing first began to loosely resemble modern processes during the Stone age (6,000 BCE), where Neolithic people manufactured pottery. The pottery technology, which produced high temperature kilns, is believed to led to advances in copper smelting.
By adding and smelting elements such as arsenic with copper ore deposits, ancient craftsmen engineered arsenical bronze. The Bronze age saw a transition from stone to metal, which was stronger and easier to shape. Similarly, the Iron Age saw widespread weapon and tool manufacturing using iron.
Ancient civilizations innovated and mass produced new technologies including the wheel and axel in and the six classic simple machines Mesopotamia, as well as Egyptian papyrus and pottery in the Mediterranean basin.
MEDIEVAL AND EARLY MODERN
In the 1960s through 1830s, the Industrial Revolution transitioned to new European and U.S. manufacturing processes. The manufacturing process transformed from hand made production to machine production powered by steam and water power. Additionally, machine tools and mechanized factory systems developed and the first industry to trial modern production methods was textiles.
After a decade-long economic recession followed by a few decades of technological innovation outside manufacturing, the Second Industrial Revolution in 1870 saw the emergence of modern manufacturing practices. Innovations included mass production, assembly lines, and electrical grids.
MODERN MANUFACTURING
The manufacturing industry gradually transitioned to modern practices in the 1890s as electricity became more practical and cost-efficient. As a result, many factories experienced a 30 percent increase in output.
Mass modern production became more attainable and consumer goods became widely available in the first two decades of the 20th century. Mass production was popularized by Henry Ford’s Ford Motor Company, which introduced sequential (or assembly line) production.
Toyota similarly innovated in the 1930s, when the car manufacturer developed lean manufacturing practices. Also known as ‘just-in-time’ manufacturing, the process reduced production and response times from suppliers.
Impacts of Manufacturing
Over the last two decades, China’s emergence as a global manufacturing leader has challenged domestic manufacturing bases.
As the deindustrialization of developed nations occurred (and continues to progress) as a result of outsourcing manufacturing offshore, employment shifted to the services sector. Many analysts believe that manufacturing is essential and raise concerns about the loss of domestic manufacturing.
Economies reap numerous benefits as a result of manufacturing including:
Economic growth is dependent upon manufacturing. In the United States, manufacturing productivity increases 3 percent each year as a direct result of technical innovation. In comparison, service industries report very slow growth because innovation is limited.
Because we have reached a point where machines can build, engineer, and maintain other machines, automation in the manufacturing industries leads to exponential economic and technological growth.
National power is also related to manufacturing productivity, which is used to generate wealth as well as military supplies and equipment. Consider that in the last 100 years, four to five of the most powerful countries have controlled three quarters of global machinery production. Some experts postulate that in the absence of manufacturing power imbalances, global power would also be balanced and result in fewer wars.
Trade relies heavily on manufacturing since goods constitute 80 percent of interregional trade, according to the World Trade Organization. Globally, countries who aren’t able to trade with other countries create large trade deficits and a reliance on other nations. Trade deficits eventually impact the value of national currency, which has trickle down effects on the cost of imported consumer goods.
Although the service industry represents the majority of global economies, manufactured goods are required to provide services. For example the business model for retail and warehousing industries (which constitute 11 percent of gross national product) revolves around selling manufactured goods. Airlines, utilities, and software companies rely on airplanes, telephone lines, and computer hardware.
Manufacturing jobs create more jobs. The Economic Policy Institute in the U.S. reports that every single manufacturing job creates three other jobs because wages are spent in other parts of the economy. Moreover, manufacturing creates middle class jobs and reduces poverty. Many manufacturing jobs are unionized, giving employees collective bargaining power.
The U.S. is one of the most innovative economies, consistently developing disruptive technology. Interest in domestic manufacturing within the U.S. is seeing a resurgence as a result of programs and initiatives aimed at rejuvenating the industry.
Industry and government leaders recognize the astounding benefits and advantages that come with a manufacturing economy. History provides assurances that investments in manufacturing innovation produce large dividends, if the American culture can rise to the challenge.
MANUFACTURE EFFICIENTLY WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Important OSHA Stats and Figures in Manufacturing
Learn these important OSHA statistics to help keep your employees safe.
Learn these important OSHA statistics to help keep your employees safe.
The manufacturing environment is often unpredictable and dangerous; workers may come in contact with heavy machinery, toxic substances, and even electrical hazards. Safety in the manufacturing industry is essential and safety standards reduce countless preventable injuries and even deaths each year.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a regulatory body dedicated to creating and maintaining workplace safety standards within the United States. It was established in 1970 to assure safer conditions for Americans.
The Bureau of Labor and Statistics reported around 14,000 work-related deaths in 1970. In contrast, the number of work-related deaths in 2018 was 5,250, despite the doubling of the U.S. workforce over that time period.
Although this progress is substantial, there’s still more work to be done to reduce workplace injury and fatalities. In 2019 alone, the manufacturing industry reported 846,700 injuries, which represents 6.6 cases per 100 full-time workers or 15 percent of all nonfatal injuries and illnesses in the private industry sector.
Benefits of having a safe workplace for employees
Safety in a manufacturing environment goes beyond checking boxes. Detailed and comprehensive manufacturing safety approaches are important for both workers and the company for a variety of reasons:
Safety protocols keep people alive and uninjured.
Safety protocols improve workforce productivity.
Safety protocols are the best way to manage risk. Safety protocols consistently minimize risks and liability, leading to substantial long-term cost savings.
Safety protocols are required by law. Compliance with OSHA regulations are mandatory, and non-compliance may result in massive fines and even jail time.
Safety protocols reduce costs. Safety incidents are very expensive and may include costs such as workers’ compensation, repairing broken equipment, regulatory penalties and legal fees, and decreased productivity. OSHA estimates that every one dollar invested in safety had a sixfold return on investment.
Preventing accidents in manufacturing
In order to realize its mission, each year OSHA releases a set of guidelines for manufacturing practices as well as facts and figures related to common violations.
SLIPS AND FALLS
Because of moving machinery, forklifts, and other obstacles in a manufacturing environment, manufacturing workers are especially prone to trips and falls. OSHA maintains industry regulations to prevent trips and falls.
OSHA guidelines aim to protect against:
Slips: a loss of balance as a result of limited friction between shoes and the walking surface (in other words, loss of traction).
Common causes of slips include:
Wet product or spills on smooth walking surfaces including water, mud, grease, oil, and even blood.
Dry product or spills, such as dusts, powders, granules, wood, or plastic wraps.
Heavily polished flooring or waxed surfaces such as concrete, marble, or ceramic tile
Sloped walking surfaces or ramps without traction
Ladders
Trips: a loss of balance caused by forward momentum after a foot hits an object.
Common causes of trips include:
Uncovered hoses, wires, or extension cords across walkways
Clutter and obstacles in walkways
Open cabinets or desk drawers
Changes in elevation or levels (such as unmarked steps or ramps)
Mounting/dismounting vehicle equipment
Falls: a loss of balance as a result of movement outside the center of balance. OSHA further segments falls into falls at the same level/surface and falls to a lower level.
According to the Bureau of Labor and Statistics (BLS), most falls are related to same-level walking surfaces. The manufacturing sector accounts for 16 percent of all injuries resulting from same-level falls.
To protect against slips, trips, and falls, OSHA guidelines mandate:
All passageways and stairways must remain free from clutter and obstacles. Handrail surfaces must be able to sustain at least 200 pounds and be finished to prevent snagging.
Businesses must maintain clean, dry floors that are free from debris and clutter. If there are surfaces that are used for water or wet processing, they must have proper drainage and mats and dry areas need to be present.
Adequate lighting is required in all walkways including stairs, hallways, and ramps.
MACHINERY GUARDING ACCIDENTS
Machines and other moving parts have the potential to cause workplace injuries including crushed limbs, amputations, burns, and even blindness. OSHA named machine guarding accidents among its top ten list of frequently cited violations and accidents.
According to OSHA, workers who operate machinery suffer 18,000 amputations, lacerations, crush injuries, and abrasion per year. Use of machines such as power saws, shears, presses, fans, conveyor belt, and palletizers are regulated. OSHA requires protection mechanisms to be in place, known as machine guarding.
Machine guarding can include barriers, light curtains, and two-hand trips and most frequently applies to the point of operation (the location where work is performed). While it’s not possible to guard some machines at multiple points, OSHA recommends secondary controls like alarms and fences.
Costs associated with workplace injuries in manufacturing
Beyond the pain and suffering of human beings, a single manufacturing safety incident may have huge cost implications for your company including:
Regulatory fines: As of 2021, OSHA penalties for violations may cost up to $13,494, however penalties for willful or repeat violations cost upwards of $134,927. Moreover, failure to correct the violation by its deadline could result in additional penalties of $13,494 per day.
Increased industrial insurance premium: each workers’ compensation incident will raise insurance premiums.
Ancillary costs associated with training replacement workers, damaged reputation, and potential lawsuits.
According to Liberty Mutual’s Workplace Safety Index, nearly a third of the same level falls represent 21 lost workdays. When factoring in all ancillary costs associated with a safety incident using OSHA’s $afety Pays website, the true cost of an accident may be several thousand times greater than the cost of preventative measures.
Safety plans can have long-lasting benefits and returns, for businesses as well as employees. Safety plans can maximize workplace productivity while minimizing risk.
OSHA training and guidelines are good keystone practices, however the most successful manufacturing workplaces create a culture of safety that goes beyond regulation.
WORK SAFELY WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Meet Vincent the Robot at Southern Automotive Conference
We’re going to the Southern Automotive Conference! Come pay us and our robot, Vincent, a visit.
We’re going to the Southern Automotive Conference! Come pay us and our robot, Vincent, a visit.
This upcoming Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday, iGAM and NRTC Automation will be in Birmingham, Alabama for the Southern Automotive Conference (SAC).
Southern Automotive Conference
Come visit our booth from October 13th to 15th, 2021!
We’ll have our beloved robot, Vincent, who can help you find the bathrooms or other vendors you are excited to see at SAC.
Vincent is named after Vital Information Necessary CENTralized, one of the main protagonists and a robot from Disney's 1979 live-action film The Black Hole.
Vincent and the iGAM and NRTC Automation team are excited to meet you. Comment down below if you are attending!
WORK WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
NRTC Receives 2021 Emerging Manufacturer of the Year Award
We are over the moon to announce that NRTC Automation received the 2021 Emerging Manufacturer of the Year Award.
We are over the moon to announce that NRTC Automation received the 2021 Emerging Manufacturer of the Year Award.
If you’ve been keeping up with our blog posts lately, then you’ll know that we were nominated to apply for the Manufacturer of the Year Award by the Business Council of Alabama.
Then, we found out we made it to the final rounds of the award process.
Well, we are honored and excited to tell you that we were chosen for this year’s Emerging Manufacturer of the Year Award!
NRTC Automation accepts 2021 Emerging Manufacturer of the Year Award
Thank you to the Business Council of Alabama, to the Alabama Technology Network, and the Alabama Automotive Manufacturers Association for selecting us for this prestigious award.
NRTC Automation is a growing business with a passion for providing expert automation services to manufacturers of any size and industry. Receiving this award underlines our commitment to provide stellar full-service automation solutions to our customers.
To read more about this award and the ceremony we attended, click the button below.
WORK WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Global Industrial Robotics: Growing and Emerging Markets
NRTC Automation reports on the current state of automation around the world.
NRTC Automation reports on the current state of automation around the world.
The International Foundation of Robots (IFR) predicts there will be nearly 4 million robots worldwide by 2022. Despite short-term declines in industrial robot adoption as a result of COVID-19, the global average robot density achieved a new record of 113 robots per 10,000 employees.
While the global outlook is promising, automation maturity is very variable from country to country.
Global Industrial Robot Market
INDIA: 4 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
Although India severely lags behind global robot density, the country is one of the fastest-growing among emerging Asian markets.
Traditionally, the strongest driver of robot installation is the automotive industry, which accounted for 44% of installations in 2018. However, the general industry, which consists of the rubber and plastics, metal, and electrical / electronics industry, has recently overtaken automotive.
The gap in robotics automation in India is commonly attributed to:
Absence of adequate hardware ecosystems: Robots require high-end components, the majority of which need to be imported into India.
Robot expense: On top of the high cost of industrial robots, import tariffs and taxes are 28.85% in India. In comparison to the low average annual wages for workers, robotics can be prohibitively expensive.
Deficit of expertise: Robotics requires specialized skills and education, which is lacking in the country.
Late to market: India entered the robotics race late, compared to other nations. Therefore, India’s robotics industry is still catching up.
MEXICO: 33 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
While Mexico lags behind the global average at 33 industrial robots per 10,000 workers, it displays modest growth. The country is expected to hit nine thousand industrial robotics sales in 2021.
Automation is most prevalent in Mexico’s automotive and auto parts sectors, trailed by semiconductors and electronics.
Mexico is one of the world’s largest economies and includes a variety of manufacturers. Since many U.S. manufacturers have moved their operations to Mexico, the country has even more motivation to further automate.
UK: 85 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
The UK lags behind major global and European competitors in its industrial robotics usage. Industrial robots in the UK are most heavily embedded in the food and beverage and automotive industry while demand is trending in manual industries such as construction.
Many experts attribute some of the UK’s stagnation in productivity (measured by GDP per hours worked) since 2008 to its slow industrial robotics adoption. When compared to nations with similar manufacturing output, the UK utilizes fewer industrial robots, and productivity suffers.
Despite lagging in adoption, industrial robotics has experienced a rise in demand. After a short decline following the COVID-19 outbreak, sales of industrial robotics in the UK increased by 52% in Q4 of 2020.
The government recognizes the importance of automation and intends to invest more of its GDP into R&D to catch up to other superpowers.
CANADA: 165 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
Canada ranks 18th in the world for robot density and is significantly above the global average in robot density (165).
Robots are primarily used in the automotive industry, where density is high. However, when the automotive sector is removed, Canada’s robot density is merely 71 and lags considerably behind other superpowers such as the U.S. The UK’s robot density is well below the global average, with only 85 robots per 10,000 employees. At that density, you’d only expect to see robots in plants employing more than 140 people.
Canada’s adoption rate is another cause for concern. Average robot density increased by just 20 units (compared to 39 in the U.S.). Although the cost of integration and lack of flexibility are significant barriers to adoption, the country is hopeful that advances in innovation will reduce blockers.
CHINA: 187 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
China is still developing robot density and currently ranks 15th in manufacturing robot density worldwide. However, China outpaces the global marketplace in its continued adoption of automation.
Industrial robotics is most prevalent in the Chinese car industry (which has been the largest in the world since 2013). It’s estimated that the industry uses a whopping 500 robots per 10,000 workers. Robotics use is also scaling in electronics and logistics, which average around 50 robots per 10,000 workers.
China’s robotics industry experience rapid growth throughout 2020 and 2021. According to the IFR “It is the fastest-growing market worldwide. There has never been such a dynamic rise in such a short period of time in any other market.” The country now accounts for 45% of all global industrial robot shipments.
While the country boasts a large workforce, the cost of labor continues to increase at a higher rate than other manufacturing countries like Vietnam. Therefore, China is incentivized to automate manufacturing to improve output and quality.
China’s long-term strategy is to support robotics startups in key industries and expand industrial robot use from traditional caged robots to robots that work collaboratively with humans.
JAPAN: 364 ROBOTS PER 10,000 EMPLOYEES
Within the last few years, Japan outpaced Germany in robot density. Despite ranking in third place in robot density, Japan undoubtedly leads the world in robot manufacturing. In fact, Seven of the 10 world’s principal industrial robotics companies are headquartered in Japan.
In Japan, even robots are assembled by robots. According to the IFR, the country’s output represents 47 percent of total global robot production.
Industrial robots are most prevalent in the electrical and electronics industry (34% share of operational stock), the automotive industry (32% share of operational stock), and the metal and machinery industry (13% share of operational stock).
Japan is also known for spearheading innovation in robotics technology. The country drives development and testing in emerging technology, such as machine vision, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
Due to this reputation, the country is considered ground zero for new robotics applications. Enterprise companies like Mitsubishi, Kawasaki, and Denso along with the government drive the continued development of industrial robotics in the country.
According to the International Trade Administration, Japan’s industrial machinery market is expected to continue to experience a growth phase. By 2065, the government is planning for a 40 percent reduction in its total workforce because of its aging population. Industrial robotics is expected to help alleviate the gap.
Start automating today
Advancements in robotics technology, emerging demand for high-quality and sophisticated products, and increasing remote and dangerous working environments will drive automation. Countries with mature or rapidly growing automation strategies will continue to thrive, while many other may be left behind.
WORK WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
NRTC Automation Finalist for Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award
NRTC Automation has reached the final round in the selection for the Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award.
NRTC Automation has reached the final round in the selection for the Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award.
We are honored and grateful to the Business Council of Alabama for nominating us for the Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award, and we’re pleased to announce that we have reached the final round!
This award recognizes outstanding manufacturers in Alabama who are committed to workplace safety, product quality, and enhancing the community.
NRTC consistently works at all three of these efforts:
We continue to uphold OSHA standards in our facilities as well as external projects
Our warehouses are audited regularly according to ISO 9001 quality assurance standards
We expanded with a second warehouse in 2020 in Birmingham, adding new jobs to the community
We’d like thank our loyal customers for choosing us as their industrial automation solution, especially through a pandemic. We are dedicated to improving our services and making it easy for our customers to meet their production goals.
Additionally, we’d like to thank our amazing employees for upholding our company values and giving our customers their best. We work as a team, and it shows.
If you are new to NRTC Automation, please check out our About Us page to get a sense of who we are, and watch our video below!
Getting Acquainted With Your New Machine: The Basics of Robotic Training
Industrial robotics training is beneficial for both business owners and your employees.
Industrial robotics training is beneficial for both business owners and your employees.
Employees often value the opportunity for paid professional development. Employers may expect benefits like reduced risk, lower employee churn, and efficiency gains.
Learn more about robotics training and how to get started with NRTC Automation below.
Programming and different robot programming languages
In order to complete tasks, robots are either guided in real time or programmed to work autonomously. Today, the majority of modern industrial robots are programmed.
While robots are typically packaged with user interface software, positional data and procedure will typically need to be programming. There are a few common programming methodologies used today:
Teach pendants: The most common method for programming an industrial robot is a teach pendant. Teach pendants are hand-held control systems with several buttons or a touchscreen. Usually, the teach pendant becomes obsolete after the robot has been programmed to perform tasks. Most industrial robots are sold with teach pendants, allowing customers to deploy them without additional software or programming.
Offline programming: A newer method that can be used to automate is offline programming. Offline programming involves the creation of a virtual simulation of the robot’s desired actions. The simulation can be created offline and deployed to the robot when refined. Because offline programming is a newer method, fewer professionals are familiar with it compared with teach pendants. However, offline programming can improve safety and limit disruptions to production.
Lead-through: Lead-through programming involves physically moving a robot through the desired actions. The technique is popular for repetitive actions along a fixed path, like paint spraying. The robot captures the positions along a path and logs them into memory to use later. Though lead-through programming simplifies programming, it has become less popular in recent years because many industrial robots have become prohibitively large to manipulate.
Because of the proprietary nature of robot software, it’s common for robot hardware manufacturers to provide their own software. For example, ABB uses RAPID, FANUC uses Karel, and KUKA deploys KRL.
While there are over 30 robot programming languages due to a lack of standardization, there are similarities between them. Typically robotic programmers are able to gain a broad understanding of programming, without learning each proprietary language.
NRTC Automation offers basic programming to advance troubleshooting to empower teams with the skills and confidence to deploy your industrial automation solutions.
Diagnostics
Critical changes that occur in an industrial robot’s system parameters can result in loss of productivity as well as unsafe manipulator operation. Therefore, monitoring and prognostics are essential for the optimal use of industrial robots.
Today, diagnostics are performed at a regularly scheduled maintenance interval, unless a critical error requires immediate action. However, the prevalence of affordable sensing technology and advanced analytics presents an emerging opportunity for fault detection.
Automated fault detection for industrial robots is challenging because it requires vast amounts of labeled training data under healthy conditions. Therefore, unsupervised machine learning algorithms, which can detect, predict, and alert on faults with high accuracy are gaining in popularity.
Repairs
Frequently, the service needs of intricate production capital are more complicated than the actual robots. Repairs are often expensive, complicated, and unpredictable. While staff may be able to handle ongoing maintenance, repairs can be complex and sometimes require years of experience to resolve.
Industrial robot repairs may involve replacing or even refurbishing components. Additionally, to avoid major delays, it’s important to have the right parts and tools on hand that may be required to fix common issues.
Common issues that warrant repairs include:
Power supply issues: Robots are powered by electricity and they use it in a number of ways, often amplifying or stepping down as needed. The electrical requirements for an industrial robot can be difficult to maintain.
CPU malfunction: Central processing units are also subject to wear and may require repairs to perform up to production standard.
Control panel errors: A number of variables can impact robotic controls, such as frequency and electromagnetic interference.
Incorrect installation or programming: Since installation can be highly technical and specialized to the facility and requirements, leaving a lot of room for error.
Mechanical failure: While many issues can be a result of programming errors, mechanical failure can cause unexpected faults.
Some industrial robotics owners choose to hire an on-staff technician to make repairs, while others decide to outsource to dedicated third-party repair companies. Many robot manufacturers and brokers also offer repair services.
NRTC Automation can conduct a top-down analysis of requirements and recommend a personalized training program to match your repair needs.
Maintenance
When it comes to industrial robots, it’s rarely possible to set it and forget it. Though robots can automate high-efficiency tasks, they require ongoing maintenance.
Regular maintenance has numerous benefits including:
Decreasing downtime
Avoiding loss of production due to undetected problems
Prolonging the lifespan of expensive industrial robots
Increasing production efficiency
Robot manufacturers list different schedules and cadences for preventative maintenance. Common industrial robot maintenance tasks include:
Tightening external bolts: Bolts and screws may loosen over time and should be tightened as needed.
Greasing joints: Periodically greasing joints with the correct grease blends will ensure smooth operation.
Testing and replacing batteries in controller and robot arm
Cleaning inside and out: Over time, robots can accumulate grease, dust, and other particles which may create safety and electrical issues. Grease, filters, vents, and cooling fans must be cleaned regularly to maintain robot health.
50-cycle verification tests: A 50-cycle verification test will provide data on robot operation. The tests will surface many concerns, such as repeatability issues, that need to be addressed.
Programming, repairs, and ongoing maintenance or complex, production robotic machinery can be daunting. NRTC Automation’s personalized training programs can help you get the most mileage out of their machines and learn from experts in industrial robotics.
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION TODAY
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
How To Evaluate ROI On Industrial Automation
Learn how to calculate ROI on your industrial equipment.
Learn how to calculate ROI on your industrial equipment.
How do you know if you made the right decision by purchasing industrial automation?
You find the ROI, of course!
Calculating the return on investment is a clear way to show how your equipment is generating revenue for your company.
Learn more about the importance of ROI and how to find it below.
Calculation of ROI for Robotic Automation
Manufacturing is a difficult industry to be in, especially in the global market.
How can robotic automation help you with grow within a reasonable budget? In that same vein, what is the return for the investment that you made in automating your processes?
As a manufacturing manager or other leadership position, you deserve to know the exact ROI on an automation product that you buy.
Simple industrial automation ROI formula
The simple return on investment (ROI) formula is always calculated as a percentage.
ROI = Gains - Investment x 100
Investment
From the above formula, it is clear that the higher the percentage, the greater will be the benefits gained by the manufacturing company.
Determine a suitable time duration to consider when computing this formula. This might be 6 months, 1 year, 5 years, or longer. Longer time intervals allow a clearer picture of your ROI.
Calculating ROI may seem complex at the start, but the following steps will convince you about the quality and benefits that robots can bring to your business.
Total cost of industrial automation
Need a more complete picture of your industrial automation ROI? Find out the total expense that will be required to make your company fully automated. This includes the following expenses.
MAINTENANCE COSTS
An industrial robot requires supervision to sustain a long usable life. According to Robotic Industries Association (RIA), the typical maintenance cost of a robot is about $500 per annum.
OPERATION COSTS
Determine the power consumption of a robot per year, as well as the labor involved in programming and operating the robot.
TRAINING COSTS
To understand new machinery or a robotic model, in-depth training may be required. Sometimes it takes weeks of training to learn how to use a machine.
By taking into account these details, you can estimate manufacturing ROI more precisely.
Savings that you can make through automation
To get even more granular, determine the potential future savings of your robot.
HIGHER PRODUCTIVITY RATE
Robots work more quickly and efficiently than humans. They can take extra shifts around the clock without little to no error margin. Find out what your productivity cost savings are by comparing manual work production with robotic manufacturing.
LABOR SAVINGS
Automation industry specialist and former Engelberger Robotics Award winner Ron Potter describes ROI as long-term strategic planning of industries that want to excel.
According to Potter, an average-sized robot consumes 7.35kW of power. Average energy costs are 10 cents per kW. as per 2013 rates of industrial use, defined by U.S. Department of Energy.
That means the average expense of a medium-sized robot will be 75 cents per hour. Comparing this cost to human labor, manufacturers can save between $15 to $20 an hour on labor.
Online ROI calculator
Want a cash flow calculation but don’t have time for the details?
Check out the online ROI Robot System Value Calculator if you want to quickly determine an estimated ROI of your robot.
NRTC Automation services
Want to generate revenue in your manufacturing facility?
Work with NRTC Automation. We offer personalized turnkey automation solutions to help you meet your production goals.
NRTC will design, build, engineer, and install a custom work cell specific to your application needs. We also offer financing on our work cells so you can automate on a budget.
Our experts will guide your team in robotics education with hands-on experience. Training is provided both on our site as well as at your desired location. Give your employees the confidence to solve all technical issues, starting from basic programming to complex diagnostics.
Give your old machinery reconditioning treatment to extend usable life and reduce costly repairs with NRTC’s Industrial Robot Refurbishing Services.
Instead of spending valuable time storing and managing extra tools and equipment, send them to NRTC Automation. Your machinery will be stored in a climate-controlled space, and we’ll send it back as soon as you need it.
Automate your facility
By following our guidelines and trusting in our robotic automation technology, you will be able to lower your production waste and boost your revenue.
NRTC Automation is a trusted partner of top auto manufacturers around the world and is here to automate your company for you. So what keeps you waiting? Contact us now if you want to keep up with the pace of the advanced industrial world.
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION TODAY
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Why Should You Consider Financing?
Manufacturers of any size can finance to enhance production and grow their bottom line.
Manufacturers of any size can finance to enhance production and grow their bottom line.
Optimization is the key to growth in manufacturing.
However, how do you continue to optimize your production line when your budget is stretched to the limit?
Financing allows facility managers to continue to improve manufacturing processes without overstepping the budget.
Learn more about the benefits of financing and how you can finance a custom work cell for your facility below.
Financing industrial automation equipment
Financing versus buying
Financing is the process of applying for a monthly payment plan with payments that are lower than the original lump sum of the product.
Buying outright might make sense in some cases. For example, purchasing several custom work cells in one payment may make sense for mid-sized manufacturers who have the revenue to support that purchase.
Other smaller businesses may struggle to add the equipment they need to their facility due to budget constraints, so they may consider financing instead.
Benefits of financing
Financing is useful for manufacturers of all sizes, phases, and industries.
Low monthly payments: Financing offers lower payments, making industrial automation more accessible for everyone.
Flexibility: With the ability to finance, manufacturers have greater flexibility in their budget to acquire the equipment they need.
Immediate growth capabilities: Manufacturers don’t have to wait until they reach a certain profitability before they expand. Financing allows them to build custom robotic work cells so they can start growing sooner.
Enhanced productivity: Finally, financing equipment enhances productivity because it quickly adds equipment to production that improves throughput and capacity.
Drawbacks of financing
As long as you are purchasing the right equipment, there aren’t many drawbacks to financing.
One downside may be that your purchase is extended across several months rather than at one time, which may make tracking the payments difficult.
However, as long as your budget is in line and orderly, you shouldn’t have to worry about missing a payment.
How to finance with NRTC Automation and iGAM
Are you looking to jump into automation, but don’t know where to start?
NRTC Automation can guide you from start to finish. Our Automation Services will get you on the fast track to start increasing throughput and capacity in your facility. We’ll work with you to design, build, and engineer a custom work cell for your production needs.
We work with top auto manufacturers like Toyota, Ford, and BMW, as well as small- to mid-sized manufacturers looking to grow their businesses. With over a decade of experience, and with our professional engineers and technicians, we provide some of the best automation solutions in the industry.
Need equipment now to boost production? Great! Our sister company, iGAM, is here to help.
iGAM provides two ways to finance:
Fill out the quick application on the product page and choose the best financing plan from the nation’s top lenders.
Apply for credit with our partner Behalf and purchase any equipment you need while making low monthly payments.
Get ahead of the competition and start automating with iGAM and NRTC Automation today.
Build a work cell for your facility
Use NRTC Automation’s Financing Services to minimize downtime and increase throughput on your production floor.
Interested in learning more about what NRTC offers? Schedule a free consultation with us by clicking the button below to get started.
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION TODAY
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Decommissioning Prep with NRTC
Get a clean, spacious facility without the hassle with NRTC Automation.
Get a clean, spacious facility without the hassle with NRTC Automation.
Tear outs don’t have to be complicated. With NRTC Automation’s tried-and-true process, we will complete your decommissioning project within your time requirements with a professional and attentive team.
To make the tear out process faster and easier, check out our steps below on how to prepare for a tear out for the best results.
NRTC’s decommissioning process
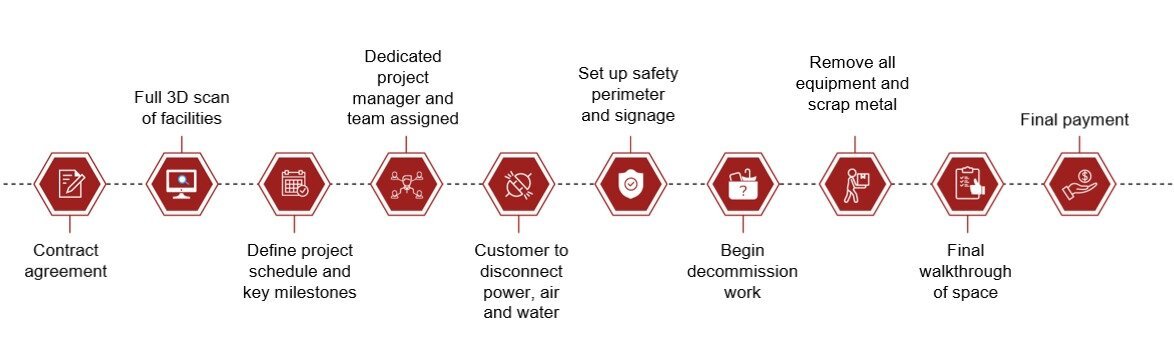
Before the start of the project
NRTC recommends that you check off these necessary tasks before a tear out:
Obtain approval: Before a facility is decommissioned, it’s necessary to obtain all approvals from the board and management teams required to move on with the decommissioning process.
Determine the use of the facility: Will your company reuse the facility for a new project, or will a new manufacturer move in to take over the space? Alternatively, the facility may be demolished. Understanding the next phase for the facility will help you plan for the remainder of the tear out.
Figure out your time constraints: Your timeline will be based on the future use of the facility. If another manufacturer or another build is moving into the space, then you will want to leave some room between the end of the decommissioning project and their move-in date.
Manage assets: Decide which equipment will be transferred to another facility for reuse. Once you have completed that step, the remainder of the equipment will be managed by NRTC Automation during the decommissioning process.
Once these tasks are complete, NRTC can start the decommission of your facility.
NRTC in the warehouse
Our Decommissioning Services are thorough and efficient to ensure that we meet your timeline while providing a broom-ready facility at end of service.
3D facility scan: Our 3D technology will provide a layout of your facility as well as photos of all your equipment, allowing NRTC Automation to complete the tear out without delay.
Project manager and team: NRTC will assign a project manager to see your tear out from start to finish. Your project manager will be dedicated solely to your project, as will a team of certified professionals in the manufacturing and industrial automation industries. Our team members will be available throughout the entire project for your tear out needs. You can easily identify them with our NRTC Automation branded safety gear.
Defining key milestones and schedule: Your project manager will define key milestones for your project to keep you updated on the progress of the tear out, as well as a definitive schedule based on your time requirements. The timeline you define will be the one we follow as we decommission your facility. NRTC Automation’s project managers are industry professionals with years of experience to aid you in your tear out. With constant updates on your progress, you’ll never have to worry about the project being sidetracked.
Prioritize safety: Just before the tear out begins, NRTC Automation will post safety signage and set up perimeters to protect our team and yours in dangerous work zones. As mentioned, our team will also wear branded safety gear for easy identification and security. Safety is our priority. Taking precautions as listed by OSHA will allow our team—and yours—to work efficiently without accident or injury.
Check out this graphic to visualize our streamlined process.
NRTC Automation takes your tear outs seriously. That’s why we use our proven process used with partners like Toyota and Mercedes-Benz to clear out your facility.
Once these steps are complete, NRTC will remove equipment and scrap from your facility for a clean warehouse ready for your next project.
Work with NRTC for expert service
Use our checklist above to prepare for NRTC’s Decommissioning Service. Being prepared means you’ll get the most return on your tear out, allowing for a faster process and greater savings.
TALK TO OUR TEAM TO LEARN MORE
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation by clicking the button below.
6 Cybersecurity Methods for Manufacturers
Protect your data and equipment from cyberattacks by using these six recommended cybersecurity methods.
Protect your data and equipment from cyberattacks by using these six recommended cybersecurity methods.
With the rise of IoT and connected industrial automation, manufacturing has becoming more efficient than ever, improving efficiency and cutting down on waste.
Unfortunately, technological advancements come with a hefty price: cyberattacks threaten to destroy companies by exploiting data and damaging industrial assets. For example, the recent cyberattack on the Colonial Pipeline in Texas shook the manufacturing sector after it shut down the pipeline.
Thankfully, manufacturers can avoid these attacks by implementing cybersecurity practices into their businesses. Learn more about the importance of cybersecurity in manufacturing below.
Get smart with cybersecurity tips
What is cybersecurity and when did it become a concern?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting and securing internet-connected systems, programs, data, and networks from malicious cyberattacks.
Malicious individuals or groups, commonly known as attackers, hackers, or cyberthreats, attempt to infiltrate systems through methods such as malware, ransomware attacks, and social engineering.
Malware is software that can harm a computer or network. Ransomware attacks are when hackers lock an individual’s computer and demand payment or information to unlock it. Social engineering uses trickery and human interaction to coax individuals into falling for attacks.
Cybersecurity became a concern in manufacturing in 2010 when Iranian PLCs were hacked by computer “worms” called Stuxnet that made sensitive data vulnerable and caused centrifuges to self-destruct.
After this attack, the manufacturing world convened to raise awareness about cyberthreats and encourage companies to protect their systems.
Why is cybersecurity so important in advanced manufacturing plants?
Manufacturing is the most common targeted industry for cyberattacks.
As manufacturing progresses with more integrated systems and the advancement of IoT technology, manufacturing plants and facilities are becoming even more vulnerable to attacks like Stuxnet.
By establishing secure systems, programs, and networks, manufacturers can continue improving their processes with smart tech without the fear of an attack. Other benefits of practicing cybersecurity and risk management include:
Protection of your employees’ data
Improved recovery time after a breach
Confidence to use data to pursue more efficient manufacturing conditions
How to secure your systems and data against hackers
Set up your business for success by taking the time to secure your internet-connected devices and equipment against hackers.
Take these steps to improve your security and protect your data:
Perform a risk assessment to determine your current level of security.
Hire a cybersecurity professional and integrate them with your IT department. They can develop firewalls and other security frameworks to defend your systems.
Educate employees on how to avoid cybersecurity attacks, such as phishing.
Become knowledgeable in cybersecurity literature and standards, such as those by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Consistently monitor and evaluate potential security threats.
Be prepared for a breach. Practicing exercises such as simulations will prepare your teams for a breach and ensure that every team member acts accordingly.
Staying on top of security is a constant yet necessary task. By adding these routines and practices into your manufacturing business, you can protect precious data and assets from exploitation while continuing to grow your business.
Want to start on the path to a smarter factory?
NRTC Automation’s sister company, iGAM, offers a vast inventory with affordable and quality industrial equipment to automate their production lines.
If you want to view data from your production lines, check out our supply:
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs)
Make informed decisions to your production line with real-time data with the right equipment.
Plus, iGAM offers two methods to finance your purchase:
If you want to finance with top lenders in the nation, click the “Finance” button on the product page and fill out our short application.
Open a line of credit through Behalf. Create an account with Behalf and get the equipment you need with iGAM.
CONTACT NRTC FOR GUIDANCE WITH INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation with us to get started on your automation journey for enhanced productivity and capacity.
3 Sneaky Manufacturing Costs to be Aware Of
"Before anything else, preparation is the key to success." — Alexander Graham Bell
"Before anything else, preparation is the key to success." — Alexander Graham Bell
Money is the energy that allows companies to grow from small businesses to large organizations that have influence in their industries. That’s why manufacturers should do everything they can to manage costs effectively.
With a bit of preparation, manufacturers can achieve their production goals and increase their customer base.
Learn more about the three sneaky costs in manufacturing below to prepare for growth.
3 costs in manufacturing
Preparation is key
If you want to grow your company, you need to lay the foundations for success.
Part of that foundation is knowing what you are up against and being prepared to meet challenges as they arise, such as expenses.
For small- to mid-sized manufacturers, this is a necessary skill to have to manage costs during the first stages of growth.
Stay competitive with leaders in your industry by charting these costs ahead of time.
3 costs to be aware of in manufacturing
1. Rent
Rent is a major expense.
Warehouse square footage isn’t cheap; in fact, the average rent paid per square foot in 2019 was $6.36, which for a facility on the small side comes out to over $30,000 per quarter!
That’s a whopping $120,000 a year just to shelter your production process.
With that knowledge, do you really want to waste the precious square footage you have?
Plan out your floorplan to optimize your warehouse space. Of course, you should always maintain OSHA standards by allowing enough room between equipment and walking space.
However, there are other methods to fit more production capacity on your warehouse floor. For example, you can store materials and equipment that aren’t being used elsewhere, such as with NRTC’s Industrial Tool and Fixture Storage solution.
Additionally, consider adding a second level to your warehouse if you have the space. Using access structures such as steel platforms and stairs allow you to optimize the vertical space in your facility, giving you the biggest bang for your rent.
2. Maintenance and repairs
According to a Delaware study, maintenance is the largest controllable expenditure in a manufacturing facility and exceeds the annual net profit in many plants. It’s estimated that maintenance costs are between 15 to 40 percent of total production costs.
On top of that, if you don’t perform maintenance correctly, then repairs (or “reactive maintenance”) are even more expensive. Eventually, equipment that isn’t maintained may need to be replaced entirely, which can sink a company that isn’t expecting that large expense.
Some ways to reduce maintenance (and repair) costs is to simplify procedures, create a maintenance schedule for predictive maintenance, and follow protocols to prevent unnecessary injuries to employees or damage to equipment.
For example, according to the U.S. Department of Energy, predictive maintenance saves up to 40 percent over reactive maintenance, making it the clear choice to save costs on equipment.
3. Downtime
Downtime, especially unplanned downtime, can be a killer.
Why? Because the average cost of a downtime incident is $17,000. Considering how 70% of manufacturers don’t maintain their equipment properly and suffer downtime as a result, that means money is burning when it could be used productively.
Downtime is inefficient: when equipment isn’t working, lead time is increased. That creates angry customers who expected to receive their products on time. The worst-case scenario of downtime is losing customers and ultimately losing revenue.
So, how do you battle unplanned downtime?
As mentioned, maintain your equipment using predictive maintenance for the best results.
Train your employees so they have a keen eye for equipment malfunctions and are better prepared to get your production line back up and running.
Finally, use production data to optimize manufacturing processes for high efficiency.
Choose to be a winner
NRTC Automation encourages manufacturers to be prepared in every area of the production process to see success in their business.
Managing costs through preparation will allow manufacturers to make better use of their warehouse space, actively engage in predictive maintenance, and see a reduction in downtime.
Use the tips listed above to enhance your facility. If you need help knowing where to go next, contact NRTC Automation to get expert advice and guidance to reach the next level.
Stay on track with NRTC Automation
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation by clicking the button below to start exceeding your production goals.
How Do Manufacturers Recycle Waste Materials?
Waste in manufacturing is an unfortunate reality. However, manufacturers can actively mitigate the effects of waste by recycling.
Waste in manufacturing is an unfortunate reality. However, manufacturers can actively mitigate the effects of waste by recycling.
Even the leanest manufacturing facilities create waste. Companies, families, and individuals all play a role in the buildup of waste.
However, that doesn’t mean we should give up and let the waste go to the landfill.
Recycling industrial waste is an opportunity to redeem useful metals, glass, and other materials from the scrap produced during manufacturing.
Learn more about how to recycle industrial waste and how NRTC Automation can help below.
Recycling in manufacturing
Source of industrial waste
Industrial waste is produced by manufacturing companies, construction sites, and production and power plants. The waste can be a by-product of manufacturing, like raw materials such as metals, or it may be broken and defective equipment that cannot be repaired.
When a company finishes a project and completes a tear out of their facility, there is a huge opportunity for recycling materials. Recyclable industrial waste is also produced on a day-to-day basis as production occurs and scrap material is left over.
What is tear out waste?
Tear out waste is any material that is not part of the company’s valuable equipment or resources.
Waste can be anything from scraps of manufacturing material to profitable materials like copper, or even remnants from lunch break. It’s important to identify waste production to prevent future debris and to save money and materials. Perhaps it is even more important to identify how to correctly manage waste so that resources are used and energy is saved.
Defining the end-state
One of the most important parts of decommissioning a project is defining the end-state. The end-state is the goal of the project: a broom-ready facility prepared to take on a new project. Defining the actions that need to happen to get to the end-state will outline our strategy for completing a tear out.
The end-state is also necessary for considering how we deal with tear out waste. In order to achieve a broom-ready facility, we will need to manage waste in a way that is both efficient and environmentally responsible.
Common recycled industrial materials
A few of the common industrial materials that are recyclable include:
Scrap metals (copper, iron, aluminum, etc.)
Glass
Plastics
Scrap tires
Chemicals
Digital waste
Most manufacturing by-product can be recycled, which makes it even more important for manufacturers to take action and recycle their waste.
Chemical waste in particular is necessary to recycle, or at least dispose of responsibly, because of the risk of contaminating groundwater and other resources.
Recycling process
Recycling is a standardized step-by-step process from picking up the waste to presenting repurposed materials to be used for new products.
Once the materials have arrived at the processing center, they are dumped and sorted. The sorting process may be done by hand or with automated lines.
The waste will then be processed once it has been accumulated into groups. Waste can be broken down, melted, or separated by parts and reused.
Finally, the waste is transformed into a useable product and can be sold to companies that utilize recycled materials to create new products and be reintroduced to the market.
Repurposed products
Recycled materials can be reused to create repurposed products, such as:
building materials
industrial equipment and storage
glass products
cables
Using repurposed products are cost-effective and marketable for being sustainable.
Let your customers know your green habits! They may be more loyal customers if they know you are doing your part to improve the sustainability of your company.
Prevent waste by recycling usable materials.
You can contribute to the movement toward a sustainable world by recycling viable industrial waste.
Conforming to the Superfund law and keeping waste out of landfills will allow materials to be repurposed, preventing more pollution and litter from soiling the planet.
DO YOU NEED PROFESSIONAL SERVICES TO DECOMMISSION YOUR FACTORY?
NRTC Automation is renowned for our decommissioning and tear out services. We provide tear outs for all industries in factories and manufacturing facilities around the world. With our dedication to complete the project on your time requirements, our strategic planning process, and our team’s commitment to your project, it’s no wonder that we are trusted by the world’s top automobile manufacturers.
Contact NRTC Automation today to discuss how we will decommission your factory according to your standards.
Top 3 Modern Innovations in Industrial Automation
Industrial automation is constantly changing and adapting to our needs with landmark innovations.
Industrial automation is constantly changing and adapting to our needs with landmark innovations.
Comparing early industrial robots to automation of today is a direct representation of how quickly technology has developed in the past few decades.
As a result, manufacturing has changed drastically across all industries. Advanced automation and software have made success available to more manufacturers around the globe.
Learn more about the history of industrial automation and some of the top modern innovations today.
Top 3 modern innovations in industrial automation
How long has industrial automation been around?
Forms of industrial automation have been around for centuries. For example, in 1856, the two-horse straddle row cultivator was patented, a device that made the back-breaking work of turning soil much easier for farmers.
Industrial automation has a long history of helping humans make work simpler and more efficient.
In the 1960s, an invention was brought to the market that would change the face of manufacturing forever.
Unimate, the first industrial robot, was patented in 1961 by the late George Devol. With a simple arm and controller design, hundreds of Unimate models performed diecasting applications on General Motors production lines.
Modern day industrial automation
One invention led to another, and now we have several top name robot brands, such as KUKA, ABB, and FANUC.
These companies are consistently producing new models with cutting-edge technology. Changes include software, end of arm tooling material, robotic vision, artificial intelligence, design, and more.
While each industrial robotics company is unique, they all have the common goal of making manufacturing as lean, efficient, and safe as possible.
Plus, robotic work cells make it even easier for manufacturers to automate without having to piece together the parts.
NRTC Automation can design, build, and engineer a custom work cell to suit your production needs. Learn more about our Automation Services here, and check out our YouTube video below!
Top 3 modern innovations
There is a plethora of fascinating developments in robotics today. NRTC Automation lists three of them below.
1. COBOTS
Collaborative robots, or cobots for short, are named for their collaboration with human workers.
Industrial robots can be dangerous to work with due to their heavy weights and movements, but cobots are specifically designed to safely work with humans on repetitive and monotonous tasks.
Cobots achieve this with advanced software that make them highly sensitive to humans working nearby.
2. BUILD-YOUR-OWN ROBOT
Now, you can build your own fully functional robot with a kit produced by Professor Neil Gershenfeld and researchers from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
Inspired by the 20 amino acids that make up all living beings, Gershenfeld created a kit composed of only five parts: rigid and flexible components, a coil, electromagnetic parts, and a magnet.
Gershenfeld and his team are now working on developing a manufacturing robot kit that technicians and other production staff can assemble and disassemble with ease.
3. ADVANCED GRIPPING SENSORS
Watching a robot handle an egg with gentle care is a sight to behold.
With soft “fingers” and advancing gripping technology, these robots can pick up and place a raw egg without cracking the shell.
The food manufacturing industry benefits from these sensors since breaking certain foods like pretzels, chips, and other fragile foods can severely affect production output.
Meet your production goals with NRTC Automation
NRTC Automation can help you create a fully customized work cell for your unique production line. We use refurbished robots and equipment so manufacturers of any size can afford to automate their facilities.
Learn more by visiting our website or give us a call at (888) 990-7606.
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATION TODAY
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Click the button below to schedule a free consultation with our automation experts.
How Industrial Equipment Can Help You Make Safety a Priority
Thousands of work-related injuries and deaths can be prevented each year with industrial equipment.
Thousands of work-related injuries and deaths can be prevented each year with industrial equipment.
Manufacturing can be a dangerous industry to work in.
Machinery is constantly in motion and chemicals of all kinds are used to manufacture products and materials.
OSHA created standards to protect workers from these potential hazards, and with industrial equipment, manufacturers can align their facilities with these standards.
Learn more about OSHA’s standards for manufacturing and how industrial equipment can help you meet your safety goals below.
Safety in industrial environments
What safety standards are set in place?
OSHA, or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, is a governmental body dedicated to workplace safety standards in the United States.
Prioritizing safety is important for all industries, but it is especially necessary in construction and manufacturing due to the dangers present in the workplace. NRTC Automation upholds safety as the number one priority in all our services.
Listed below are the top safety standards that all manufacturing facilities are expected to use:
Lockout tagout (LOTO): LOTO are procedures used to prevent equipment from running during repairs and maintenance as well as to prevent spills and leakage of hazardous materials. A lockout device will keep unaware individuals from attempting to use to machinery or materials. A tag will include information about who created the tag and the time of placement. A thorough inspection must be performed if the tag is to be removed.
Permit-required confined spaces (permit space): Workplaces with spaces that are too small for people but large enough for workers to perform tasks is considered a confined space. These spaces require permits from OSHA for workers to access. Examples of confined spaces are pipelines, tunnels, and tanks. They may have some of the following characteristics: exposed live wires, heat stress, converging walls or sloping floors, and more.
Personal protection equipment (PPE): PPE is gear worn by workers to protect them from injury and death. There are different PPE designed for specific hazards, including heat, impact, optical radiation, chemicals, and dust. Common PPE worn by manufacturing workers include safety goggles, face shields, and hardhats.
Machine guards: Using machine guards is especially important in manufacturing where machines are constantly working around human workspaces. There are over 800 deaths per year that could have been prevented with a machine guard. There are several parts that needed to be guarded on a machine, such as the point of operation and around any blades. Each piece of equipment is unique in what machine guards it requires.
Warning signs: OSHA requires certain warning signs to be used in areas where there are hazards such as dangerous chemicals or heavy machinery. They must be able to be universally understood, like using a bright yellow color for caution signs and red for danger signs. Manufacturing facilities must also contain signs for first aid stations and emergency eye wash stations.
Employee compliance: Last but certainly not least, employee compliance is an important part of maintaining a safe facility. Employees must first be aware of the safety standards required by OSHA and the employer must provide the necessary PPE and other tools to keep employees safe. Then, employees must conform to safety standards to protect themselves and others from harm. OSHA inspectors can inspect a facility without warning to ensure safety standards are being met.
With these safety standards set in place, manufacturing workers can perform their jobs without fear of injury or worse, creating a productive and efficient facility.
How industrial equipment can help you make safety a priority
Industrial equipment can do more than increase throughput and capacity in your facility. It can also help you prioritize safety for your workers.
1. INDUSTRIAL EQUIPMENT CAN MAKE WORKSPACES MORE ERGONOMIC.
According to OSHA, workspaces lacking ergonomics are a significant cause of musculoskeletal disorders (MSD) and injuries; in fact, they are the most frequently cited cause of lost productivity.
Using industrial equipment to enhance the ergonomics of your employees’ workspaces is key to preventing potentially long-term injuries. For example, a turntable provides easy access to materials or equipment while helping workers waste less energy and time on extra movement.
Check out iGAM's Fibromat Heavy Load Positioning Turntable for a great deal on safety equipment for your employees.
2. INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS CAN HANDLE THE REPETITIVE TASKS.
Industrial robots are designed specifically for repetitive tasks like material handling, welding, and more.
Repetitive tasks are another source of MSD and injuries. For example, material handling can cause shoulder problems that affect workers for a lifetime.
Additionally, repetitive tasks can be dull and cause workers to drop their attention, which can not only cause problems for product quality and productivity, but it can also pose serious risk to the workers’ health.
By adding an industrial robot to your facility, you can increase productivity while protecting your workers from unnecessary harm.
3. INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS CAN ALSO HANDLE THE HEAVY LIFTING.
Industrial robots, such as this R-2000IC-210F FANUC robot, have a payload capacity of several hundred pounds. Some robots can even lift several tons!
With an industrial robot, you can ensure that heavy materials, parts, products, or equipment are expertly handled without fear of harming your employees.
4. ACCESS EQUIPMENT PREVENT FALLS.
Finally, industrial access equipment such as stairs, lifts, platforms, and ladders assist manufacturing workers with getting to hard-to-reach places without putting themselves in danger.
Falls are the leading cause of death in construction. Along with the right safety gear, access equipment can prevent tragedy in the workplace.
Visit iGAM to shop for stairs, ladders, and platforms for your employees.
Get on top of safety in your facility
Creating and maintaining a safe work environment requires consistent effort and vigilance. However, it’s well worth it when your employees are satisfied knowing their safety is secured.
Work with NRTC Automation and iGAM to protect your employees, no matter what size, phase, or industry you’re in.
SCHEDULE A FREE CONSULTATION WITH NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Visit NRTC Automation today for full-service solutions to improve productivity in your facility.
We’ve Been Nominated for Manufacturer of the Year Award
NRTC Automation is honored to be recognized for our commitment to our customers.
NRTC Automation is honored to be recognized for our commitment to our customers.
We are excited to announce that the Business Council of Alabama has nominated NRTC Automation for the Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award!
NRTC Automation serves the local Alabama community from our Birmingham warehouse, as well as internationally.
It is an honor to be acknowledged for our efforts, especially during a pandemic. NRTC is known for our dedication to quality service and expertise in industrial automation and decommissioning services.
We thank the Business Council of Alabama for our nomination and continue to offer our customers the best service we can provide.
Learn more about the award and NRTC Automation’s services below.
Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award
What is the Alabama Manufacturer of the Year Award?
This award has been offered annually since the turn of the 21st century.
According to their website, the awards “recognize the state's top manufacturers for their accomplishments. By applying for the award, manufacturers convey their story of financial growth, manufacturing leadership, market leadership, leadership development, and workforce enhancement.”
Sponsors of the award include the Alabama Technology Network, the Business Council of Alabama, and Alabama Automotive Manufacturers Association.
This award supports Alabama’s manufacturing industry by recognizing the achievements of manufacturers, promoting better products and service to the public.
NRTC Automation is proud of our commitment to our customers
At NRTC Automation, we help manufacturers maneuver through the world of automation. Your growth is our mission.
We provide a customized solution for the decommissioning and tear out of your manufacturing and industrial assets. Our focus is on minimizing disruption and downtime in the work area while emphasizing safety, speed, and efficiency.
We also provide additional services to help ensure full adoption of automation solutions and a seamless integration into your workplace, such as:
NRTC was founded over a decade ago in Tilbury, Ontario with the goal of delivering high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
With partners from small manufacturers to global manufacturers like Toyota and Ford, we have the experience needed to get you where you want your production to be. Trust us to help with your next industrial automation project.
Working with iGAM under NRTC Alabama, Inc.
NRTC Alabama, Inc. is an industrial automation services company. For over a decade, we have provided full-service solutions to assist manufacturers through every step of automating their facilities.
Under NRTC Alabama, Inc., NRTC Automation and iGAM work together to guide our customers from purchasing industrial equipment and parts to optimizing their production lines.
iGAM is the online marketplace for used industrial robots, robot parts, and manufacturing equipment. With competitive pricing, flexible financing options, and ready-to-work equipment, iGAM is the solution for manufacturers of any size looking to automate their facilities. Plus, iGAM offers asset appraisal services so customers can determine the value of their equipment.
Together, NRTC Alabama’s brands make automation accessible for manufacturers in every industry.
Follow us on social media
To stay updated on NRTC Automation and iGAM, follow us social media!
You can find NRTC Automation on:
And you can follow iGAM here:
We post several times a week, sharing the latest industry news, product sales, entertaining memes, content of our team, and more. Join in on the fun!
Also, check out our blog for more weekly articles on the industry.
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation today to have our experts assess your industrial automation needs.
Can Robots and Humans Work Together in the Real World?
Automation is a hot-button issue. Get the facts with NRTC Automation and see how robots and humans can work together for a brighter future.
Automation is a hot-button issue. Get the facts with NRTC Automation and see how robots and humans can work together for a brighter future.
Industrial robots are demonized as all-knowing machines determined to destroy families.
While the news may not help this image, reading studies and learning about how industrial robots actually help humans in the workplace will dispel the myth.
Get an inside look at how industrial robots make human lives better below.
Working alongside industrial robots
Addressing the fear of robots taking jobs
The media, as with any controversial topic, does a fine job at creating panic over automation.
According to sources like CNN, millions of low-skill jobs are at the mercy of industrial robots in the next few decades.
Furthermore, fears of humanoid robots taking over uniquely human jobs, such as therapy, is spurred on by threats of science fiction-level artificial intelligence.
However, this is simply not the case.
“Most jobs are more complex than [many people] realize,” said Google’s chief economist, Hal Varian, during a forum on the future of work.
For example, even a simple welding job takes a considerable amount of programming and engineering for a robot to accomplish.
And it takes people to program, engineer, and fix those robots. With robotic training, workers can shift from monotonous and potentially dangerous labor to safer and more creative work.
Plus, consider the fact that there will be over 2 million unfulfilled jobs in manufacturing due to a skills gap by 2030. Unemployment is rampant, but finding workers to fill these roles is getting harder. Industrial automation can close the gap for some positions, but many others require skilled human labor.
Why humans should work with robots
One way to get around this disaster mindset is to think about working with robots, rather than fighting against them for our jobs.
Robots make life better. They can handle heavy weights, withstand extreme temperatures, and work day and night without taking a sick day. These characteristics means our fast-growing population will receive the products and services needed to maintain our quality of life.
Working with robots is becoming easier as well. With collaborative robots, or cobots, workers can perform tasks right next to a cobot without fear of injury. They are designed specifically to make a human’s job easier to perform.
Benefits of using industrial automation
Robots have a lot to offer us humans. By seeing clearly through our fear, we can appreciate how industrial automation improves our lives for the better.
1. ROBOTS PROVIDE A SOLUTION FOR UNSANITARY AND DANGEROUS JOBS.
Labor during the Industrial Revolution, which transformed our world into what we know today, was dirty, difficult, and dangerous.
Factory air was polluted with smoke and soot, regulations for labor were nonexistent, and workplace safety wasn’t considered important, leading to life-endangering accidents. Government regulations fixed many of the problems caused by the Industrial Revolution.
The development of robots in the workplace further enhanced working conditions for people by taking over heavy labor and dangerous jobs that put humans at risk. Jobs like waste management and bridge inspections are being performed by robots, protecting humans from disease, injury, and death.
Today, robots continue to make work environments safer for humans.
2. ROBOTS CREATE JOBS, RATHER THAN TAKE THEM AWAY.
As mentioned above, total automation isn’t possible. Dull, repetitive tasks such as packaging food can be automated, but more complex tasks require far more programming than most robots are capable of (or most companies can afford).
Stanford Business gives the example of a gardener’s daily tasks: mowing is easy to automate, but other chores like weeding, pruning, and watering would be too complex for one robot to manage.
Because robots have provided humans with more leisure and expendable income, industries like video games, dating applications, and gyms are thriving. This creates jobs for designers, writers, personal trainers, management, customer support, and more. These jobs cannot be automated due to the nature of the work, and they are possible because of the relief robots provide from grueling, time-consuming labor.
3. ROBOTS ENHANCE WORKPLACE PRODUCTIVITY AND BRING CONSISTENT, RELIABLE RESULTS.
By taking over the repetitive and boring work, robots allow humans to focus on the important tasks. Not only that, but robots are highly consistent and perform their jobs reliably. This allows humans to know that the job is done correctly and saves time checking for quality assurance.
Automate your facility
As you can see, industrial automation is the future of manufacturing. Robots improve the health and safety of humans while increasing productivity and minimizing downtime on the manufacturing line.
If you are a manufacturer looking to automate your facility, you’ve come to the right place. NRTC Automation can design, build, and engineer a custom work cell for your specific needs. Whether you need a single, double, or triple robot cell, we have you covered.
Alongside our sister company, iGAM, we source and refurbish used industrial robots and manufacturing equipment to create affordable turnkey automation solutions for manufacturers of any size and phase.
Plus, we offer financing so you can automate on a budget. Visit our Financing page to learn more about how you can grow your company with low monthly payments.
Check out our Automation Services video below!
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION TODAY
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation with NRTC today to learn more about how we can help you meet your production goals.
Unimate: The OG Industrial Robot
The first industrial robot opened the doors to a world of automation.
The first industrial robot opened the doors to a world of automation.
Our world has completely changed in less than a century.
Technology has made life easier in many ways. From cars to phones to elevators, daily life looks very different compared to the early 20th century.
Industrial automation is no different. Because of the Unimate, technology has made its way into manufacturing.
Learn more about the Unimate and how you can automate your facility with modern-day robots below!
Unimate, the first industrial robot in history
What is the Unimate?
The Unimate is the first industrial robot ever created in history. Its inventor, Geroge Devol, patented the Unimate in a small Connecticut town in 1961. Similar to the industrial robots of today, it had a single arm designed for repetitive tasks. The arm weighed an impressive 4,000 pounds.
The automation industry was the first to adopt the Unimate for metalworking and welding.
History of the George Devol and the Unimate
Devol drastically changed the way manufacturing processed and produced with his invention.
Devol was born in Louisville, Kentucky on February 20, 1912. He was 9 years old when the word “robot” first appeared, and, supported by a wealthy background and an interest in electricity and machines, he started building the knowledge needed to invent the Unimate.
Rather than going to college, Devol decided to start his own company. His first invention was the automatic door, or the “Phantom Doorman.”
Several years later, after World War II, Devol and his Unimation Corp. company developed a machine called the Programmed Article Transfer, which slowly evolved into a robot: the Unimate.
General Motors adopted the robot on their production lines in Trenton, New Jersey.
Devol continued to bring technology to life over the course of his career. He passed away at 99 years old on August 11, 2011.
How the Unimate changed the world of manufacturing
Thanks to Devol, the Unimate opened the doors for revolution in manufacturing. Industrial robots have been refined and expanded upon since the Unimate’s creation so that manufacturers of any industry can automate their facilities.
The industrial robots of today have far more applications compared to the Unimate’s limited offerings, including but not limited to:
Material handling
Painting
Machine tending
Picking and palletizing
Gluing, sealing, and spraying
Waterjet cutting
Assembly
Additionally, robots have made their way out of manufacturing and into other industries such as medicine. Surgeons use robots to assist with very delicate surgeries, such as head and neck or heart surgeries.
Additionally, hygienic robots have made a breakthrough during the COVID-19 pandemic, helping to keep hospitals, airports, and warehouses clean.
Because of the Unimate, the possibilities are endless for automation to create a brighter, cleaner, more productive future.
How to automate your facility
Are you new to automation, but you feel intimidated by all the options?
Don’t fret! NRTC Automation and our sister company, iGAM, are here to help.
NRTC can build a custom work cell to specifically for your production needs. We will design, build, engineer, and install the robotic work cell for you so all you need to do is turn it on!
With NRTC, automation is simple. We offer financing so you can automate no matter what size or phase you are in. Visit our Financing page to learn more.
iGAM offers standalone industrial robots as well. With top name brands like KUKA, FANUC, and ABB, you can be sure that your production line will be more efficient while reducing downtime on the warehouse floor.
Friendly iGAM Specialists are available to help you find what you need, including robot controllers, robot parts, and other manufacturing equipment. iGAM also provides financing for a pain-free transition to automation.
Need additional support after implementing robots into your facility? NRTC Automation offers full-service solutions to help you meet your production goals. From industrial robot refurbishing to robotic engineering, we’re your source for automation services. Visit our website to see everything we offer!
Together, NRTC Automation and iGAM are here to make automation accessible to all manufacturers. Work with us to start growing your company today.
VISIT NRTC AUTOMATION
NRTC Automation is dedicated to providing high-value industrial automation and manufacturing equipment solutions to all our customers.
From decommissioning and tear out to industrial robotic training services to custom flexible work cells, NRTC is the key to integrate your workplace. With personalized training and custom-built designs, NRTC Automation is the destination for all your industrial automation and manufacturing equipment services.
Schedule a free consultation with NRTC! We will work with you to create a turnkey automation solution to meet your needs.